QuantSeq is a 3’ mRNA-Seq library prep protocol, which is the method of choice for RNA-Seq gene expression analysis due to the simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and data quality offered by this technology. It has already been cited in almost 300 publications. The QuantSeq protocol has been complemented with Unique Molecular Identifiers (UMIs).
UMIs are used to eliminate possible PCR duplicates in sequencing datasets and therefore facilitate unbiased gene expression profiling. The basic principle behind the UMI deduplication step is to collapse reads with identical mapping coordinates and UMI sequences. This step helps increase the accuracy of sequencing read counts for downstream analysis of gene expression levels.
The analysis and interpretation of QuantSeq data with UMIs require specialized bioinformatics tools. Lexogen has implemented the QuantSeq-UMI data analysis pipeline in Partek Flow software, providing kit users with a simple, streamlined tool for data analysis. Similar to the previously integrated QuantSeq data analysis pipeline, access to the UMI data analysis is offered to the owners of Partek™ Flow™ licenses.
The utility of the QuantSeq pipeline in Partek Flow is emphasized by one of its users, Dr. Kenta Shirasawa from the Kazusa DNA Research Institute:
“I could analyze my Quant-Seq data with the Partek Flow QuantSeq pipeline quickly and reproducibly. The most important point is that it is possible for our lab members and collaborators who are not familiar with bioinformatics to analyze their data by themselves and to generate publication-quality figures and tables.”
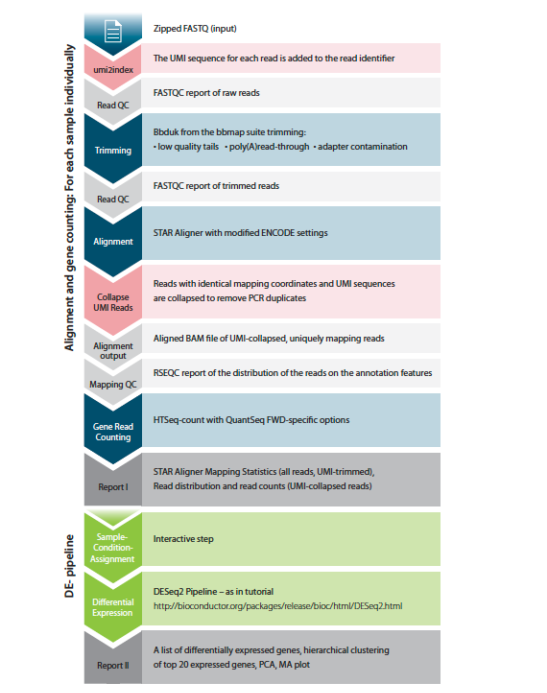
The standard QuantSeq FWD Data Analysis Pipeline steps include removal of poly-A tails and sequencing adaptors, trimming reads based on quality, aligning reads to any reference genome using the STAR aligner, and mapping reads to any public or custom transcriptome database.
The QuantSeq-UMI Data Analysis Pipeline introduces two additional steps compared to the standard pipeline:
- First, the umi2index process adds the 6 nucleotide UMI sequence to the identifier of each read and trims the UMI from the start of each read. This generates a new FASTQ file, which is then processed through trimming and alignment.
- Second, after alignment, the mapped reads are collapsed according to the UMI sequence of each read. Reads are collapsed if they have the same mapping coordinates (CIGAR string) and identical UMI sequences. Collapsing reads in this manner removes PCR duplicates.
Users can then use the comprehensive statistics and interactive visualizations within Partek Flow to explore and interpret the biological implications of the data.
